Introduction
The HTMLElement interface represents any HTML element.
The HTMLElement is an interface HTML DOM API.
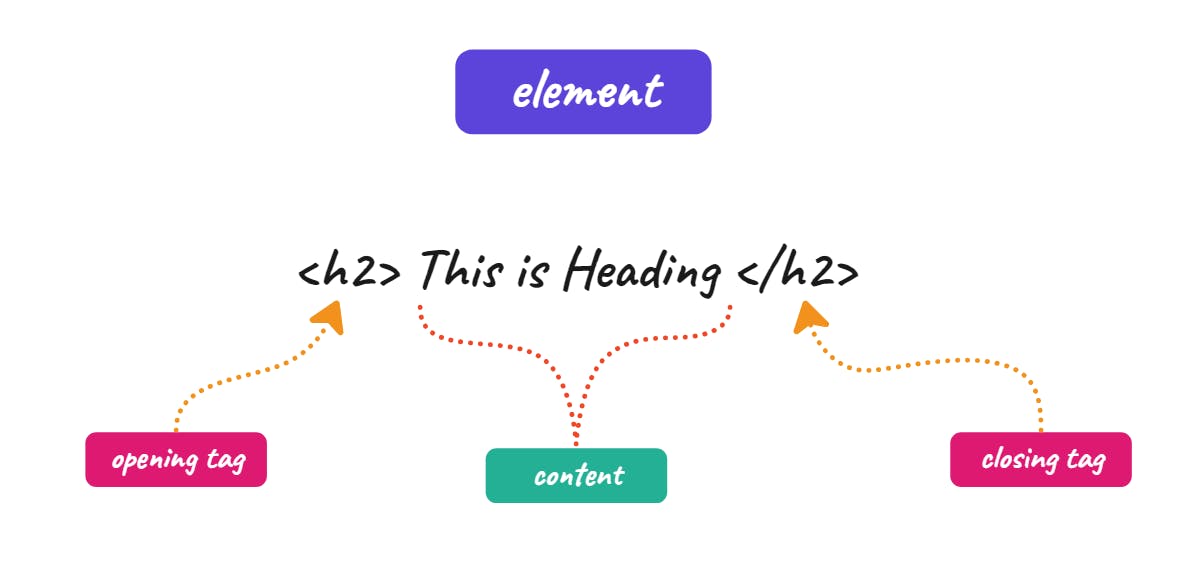
An HTML element consists of an opening tag, content, and a closing tag.
Types of element
Structural Elements
<html>
It is the root element of an HTML document.
<head>
Contains metadata about the document.
<title>
Defines the document's title.
<style>
Contains style information of a document.
<body>
Contains all the visible elements of the document.
<script>
Contains script codes of the document.
<div>
Contains a set of nested elements in the document.

Modern HTML5 Building Block
<main>
There is only one main element and it is not a descendent of any other element
<header>
It contains the introductory content.
<nav>
This defines a set of important navigation links used within a document.
<section>
It provides a division of content within the document in terms of chapters, footers, headers, etc.
<aside>
This contains content that is slightly related to the primary content or acts as a highlighter to the main intent.
<article>
It represents the independent content of a web page.
<footer>
It contains the footer for the document.

Form Elements
<form>
This element is responsible for the creation of forms.
<input>
To take inputs from the users.
Know more about Input Element (Different Types of Input)
<label>
Used to define the caption of a particular input type.
<fieldset>
To group similar elements within a form.
<textarea>
Provides the users with a typing space wherein they can write some multi-line text.
<button>
The button element is an interactive element activated by a user.

Table Elements
<table>
This is the root element for creating a table.
<colgroup>
This element is used to group a set of columns to avoid repeated formatting.
<thead>
This element specifies the header of the HTML tables.
<tbody>
This element specifies the header body of the HTML tables.
<tfoot>
This element specifies the footer of the HTML tables.
<th>
Used to define the header column in a table.
<tr>
Used to define rows within an HTML table.
<td>
Used to specify the data within the columns of the table.
List Elements
<ul>
This element represents an unordered list of items, typically rendered as a bulleted list.
<ol>
This element represents an ordered list of items — typically rendered as a number or letter.
<li>
This element is used to represent an item in a list.
It must be contained in a parent element:
An ordered list <ol> or
An unordered list <ul>.
Content Elements
<h1>, <h2>, <h3>, <h4>, <h5>, <h6> Represent six levels of section headings.
<h1> is the highest section level and <h6> is the lowest.
<a>
The anchor tag is used to create hyperlinks within a web page.
<p>
Represents a paragraph.
<span>
This element marks a particular part of the document or text.
<b>
Used to bold the contents of a particular text.
<i>
This element is used to italicize a particular content.
<u>
This element is used to give underline a particular content.
<sub>
It displays the content in subscript.
<sup>
This displays the content in superscript.
<br>
Produces a line break in the text.
<img>
Embeds an image into the document.
<iframe>
Represents a nested browsing context, embedding another HTML page into the document.
