JavaScript Functions
JS Function, Intro., Declaration of function, Types of Functions, Built-in Functions
Introduction
Functions are one of the fundamental building blocks of javascript, it's a group of reusable code that can perform some task and executed when it is been called or invoked.
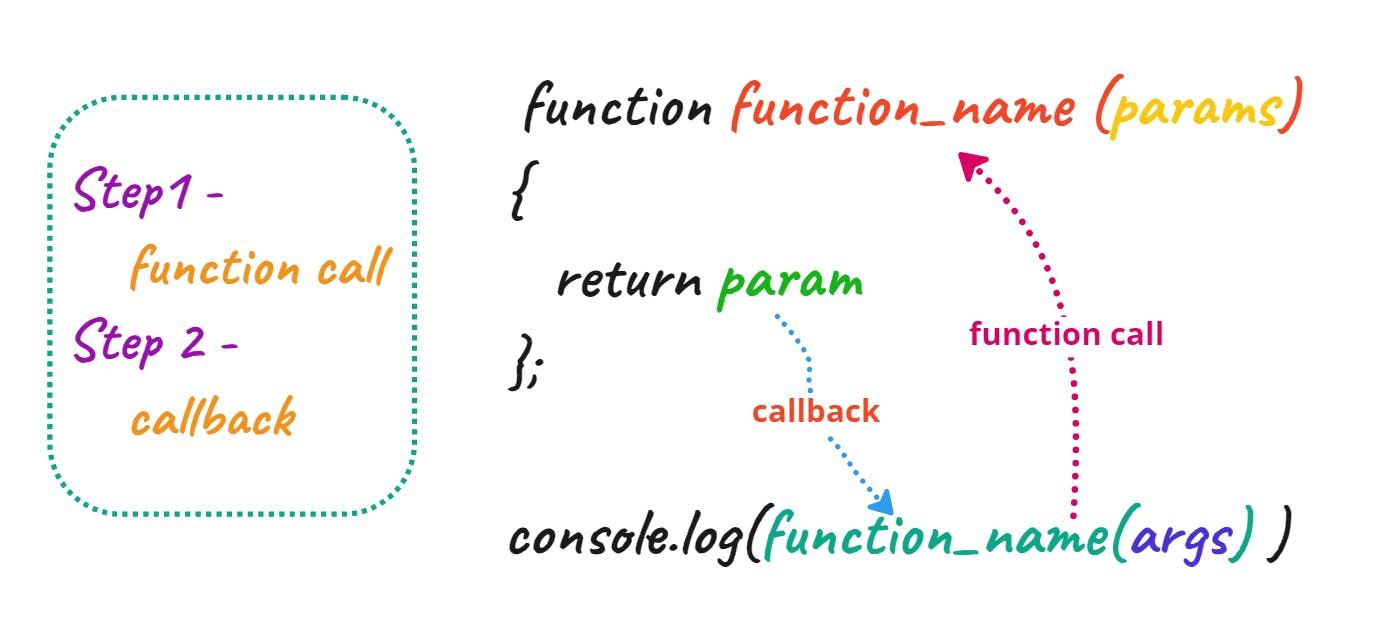
Declaration of Function
function function1()
{
return "John"
}
Calling a Function
function1()
function function1()
{
return "John"
}
console.log(function1())
Output:
John
Types of Functions
Named Function
In this function, the function is declared with by function keyword along with function name.
function function1()
{
console.log("John1")
}
function1()
Output:
John1
Hoisting Function
Function hoisting is a mechanism in which the JavaScript engine physically moves function declarations to the top of the code before executing them.
function1()
function function1()
{
console.log("John1")
}
Output:
John1
Anonymous Function
An anonymous function is a function without a name. An anonymous function is not accessible after its initial creation.
const function2 = function(){
console.log("John2")
}
function2()
Output:
John2
Immediately Invoked Function
The immediately invoked function is execute itself immediately after the declaration.
function1()
function function1()
{
console.log("John1")
}
const function2 = function(){
console.log("John2")
}
const function3 =
(function(){
console.log("John3")
})()
function2()
Output:
John1
John3
John2
Arrow Function
An arrow function is an anonymous function expression written with the fat arrow syntax ( => ).
Arrow functions are not hoisted.
const function4 = () => {
console.log("John4")
}
function4()
Output:
John4
Scope of Function
Variables defined inside a function cannot be accessed from anywhere outside the function, because the variable is defined only in the scope of the function. However, a function can access all variables and functions defined inside the scope in which it is defined.
Accessing Its Calling Scope
let name ='John'
function function1()
{
console.log(name)
}
function1()
Output:
John
Function Scope variable
function function1()
{
let name ='John'
console.log(name)
}
function1()
console.log(name)
Output:
John
ReferenceError: name is not defined
Built-in Functions
eval()
eval() is used to convert string to executable arithmetic operations.
let sum = '4+3'
console.log(eval(sum))
Output:
7
isNaN()
The isNaN() function determines whether a value is NaN or not.
let string = 'John'
console.log(isNaN(string))
Output:
false
parseInt()
The parseInt() function parses a string argument and returns an integer.
let string = '6562'
console.log(parseInt(string))
console.log(typeof(parseInt(string)))
Output:
6562
number
typeof()
The typeof() function parses an argument and returns a data type of element.
let string = '6562'
console.log(typeof(parseInt(string)))
Output:
number
